make.polyhedron¶
make.polyhedron will modify an initial topobathymetric surface by adding or subtractracting a polyhedron based on user-defined planes. The following is typical usage for make.polyhedron.
Prepare a topography file as a geotif.
Prepare or obtain a polygon shapefile indicating where the polyhedron should be applied. Ensure that the geotif and shapefile have the same coordinate system.
Determine a list of dictionaries, each specifying a plane of the desired polyhedron.
Run
make.polyhedronto modify the topobathymetry file. Inspect the output and adjust any input parameters as needed.Using these files, set up a D-Claw simulation to run and analyze.
diggerwill not do this for you.
A code snippet that uses make.polyhedron may be found in the file digger/examples/pre-run/black_lake/make_polyhedron_black_lake_example.py. In this example, a polyhedron is removed from above Black Lake.
"""An example of using digger.make.polyhedron.
This example uses Black Lake topography and provides an example of using
digger.make.polyhedron.
"""
from digger import make
# Run digger.make.polyhedron
black_lake = make.polyhedron(
topo_path="../../../data/black_lake_dem.tif",
mask_path="../../../data/black_lake_poly_ext.shp",
planes=[
{"xyz": (419848, 5129676, -50), "dip_dir": 360, "dip": -30},
{"xyz": (419848, 5129676, -50), "dip_dir": 120, "dip": -30},
{"xyz": (419848, 5129676, -50), "dip_dir": 240, "dip": -30},
],
mask_to_water=False,
sense="subtract",
write_tif=True,
write_tt3=False,
b_prefix="b_polyhedron",
q1_prefix="q1_polyhedron",
eta_prefix="eta_polyhedron",
fig_path="polyhedron.png",
)
After this code runs, it will produce geotif and topotype3 files that specify the modified topobathymetry.
It will also create diagnostic figures.
The standard diagnostic figure from make.polyhedron
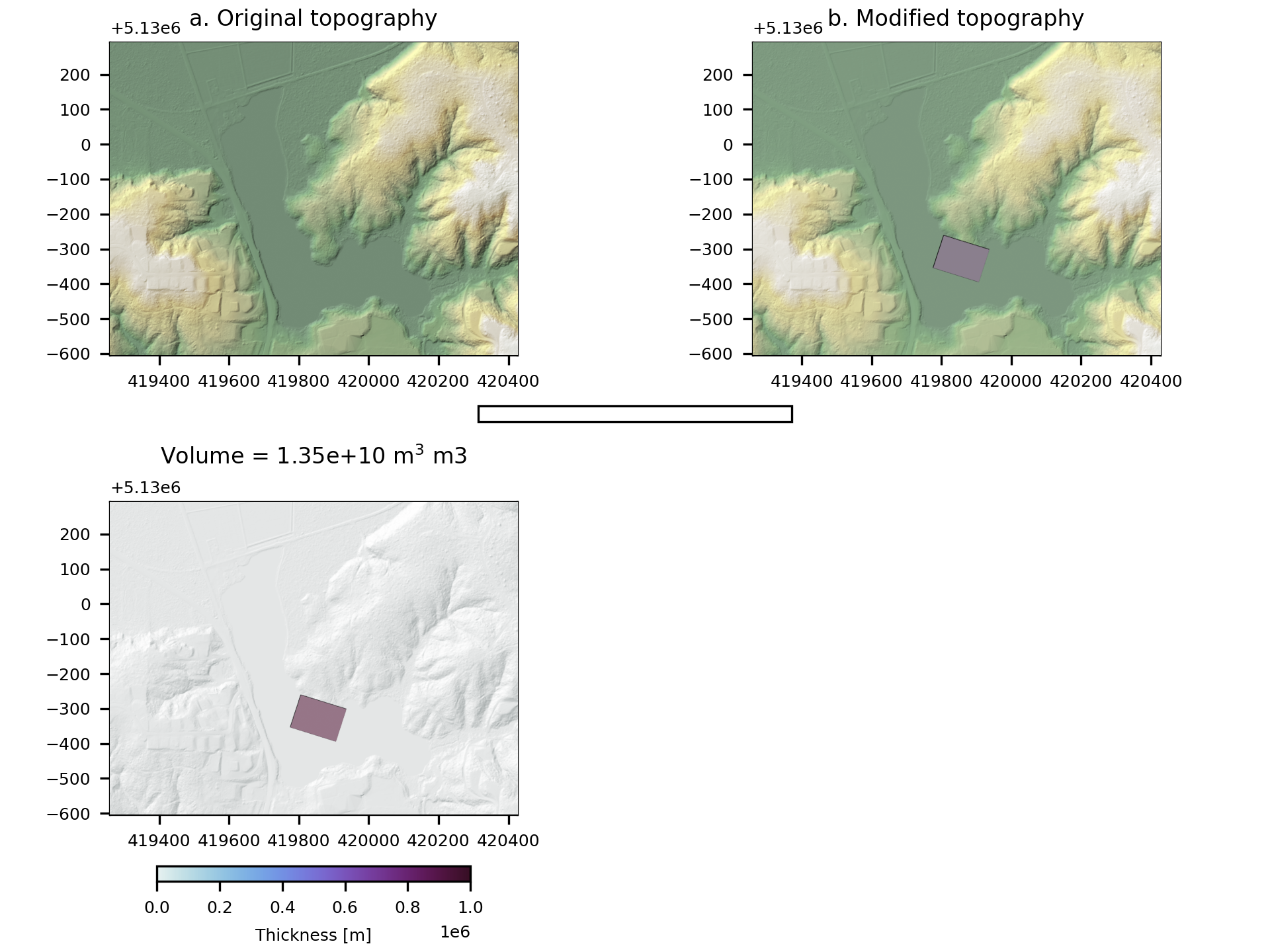
Fig. 7 An example of the diagnostic output provided by digger.make.polyhedron.¶