make.breach¶
make.breach will modify an initial topobathymetric surface by adding a breach based on user-provided polylines. The following is typical usage for make.breach.
Prepare a topography file as a geotif.
Prepare a polyline shapefile that contains information about the start and end points of each breach. Ensure that the geotif and shapefile have the same coordinate system.
Run
make.breachto generate input files for D-Claw. Inspect the output and adjust any input parameters as needed.Using these files, set up a D-Claw simulation to run and analyze.
diggerwill not do this for you.
A code snippet that uses make.breach may be found in the file digger/examples/pre-run/black_lake/make_breach_black_lake_example.py. In this example, a synthetic breach is placed across a road.
"""An example of using digger.make.breach.
This example uses Black Lake topography and provides an example of using
digger.make.breach.
"""
from digger import make
# Run digger.make.breach
make.breach(
topo_path="../../../data/black_lake_dem.tif",
breach_path="../../../data/black_lake_breach.shp",
b_prefix="b_breach",
fig_path="breach.png",
)
After this code runs, it will produce geotif and topotype3 files that specify the modified topobathymetry.
It will also create diagnostic figures.
The standard diagnostic figure from make.breach
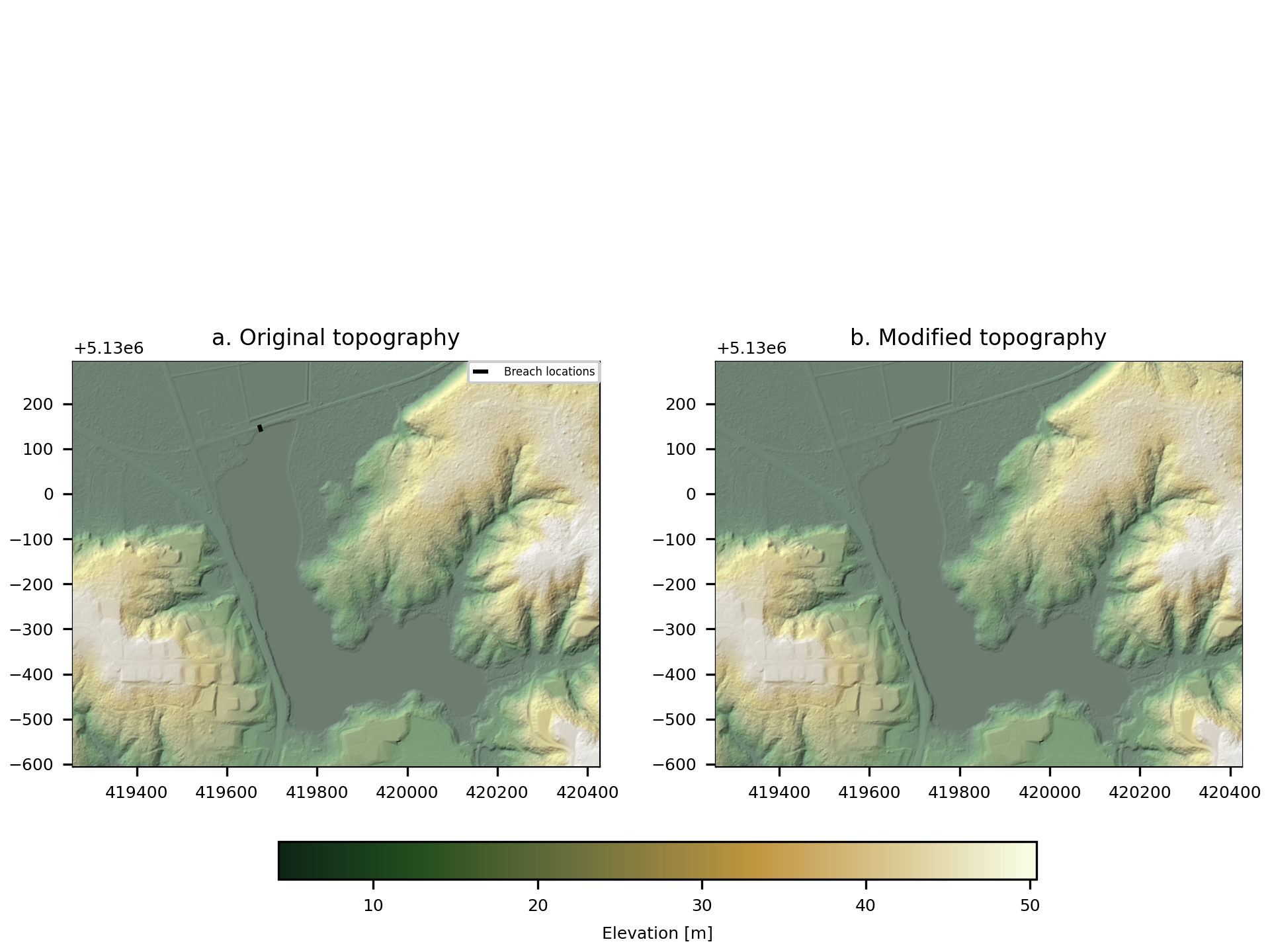
Fig. 1 An example of the diagnostic output provided by digger.make.breach.¶