analyze.spectrogram¶
The function analyze.spectrogram analyzes a numerical gauge trace using a fast Fourier transform to generate a spectrogram.
# Spectrogram analysis
import numpy as np
from digger import analyze
from digger.utils import gauge2ts
(
t,
eta,
) = gauge2ts("_output/gauge00001.txt", samprate=2)
t0 = np.min(t[eta > 0]) # wave arrival time
times, amps, xf, yf = analyze.spectrogram(
t0=t0,
simlength=np.max(t), # simulation duration in seconds
eta=eta[t > t0],
samprate=2, # sample rate from gauge2ts
gauge=1,
window=100,
waterlevel=0,
plot=True,
plotname="spectrum-BA",
)
Attention
This code snippet is not fully self-sufficient. This snippet relies on simulation output files. To reproduce the example, execute the file digger/examples/post-run/barry_arm/setpostprocess.py from within the directory in which it is located. Before the script is executed either the example simulation must be run or the file digger/data/barry_arm_output.zip must be unzipped and the resulting directory (_output) must be placed within digger/examples/post-run/barry_arm/.
The utility function digger.utils.gauge2ts assists in ensuring that the numerical gauge data provided by D-Claw conforms to the expectations of the spectrogram and wavelet analysis.
Running this code snippet generates three diagnostic figures that depict the detrended gauge, the frequency content of the gauge trace, and the spectrogram.
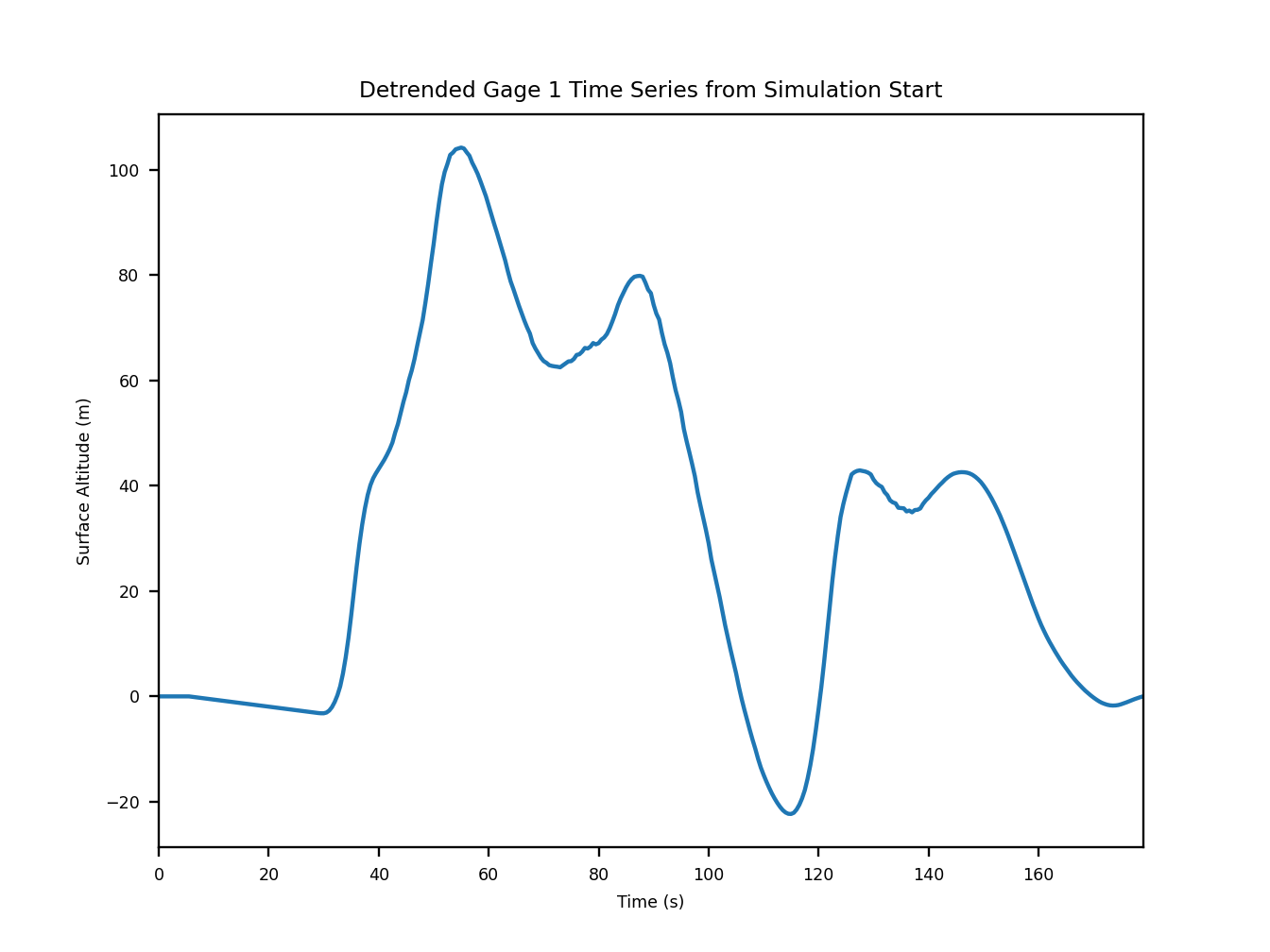
Fig. 17 An example of the diagnostic output provided by digger.analyze.spectrogram showing the detrended gauge trace.¶
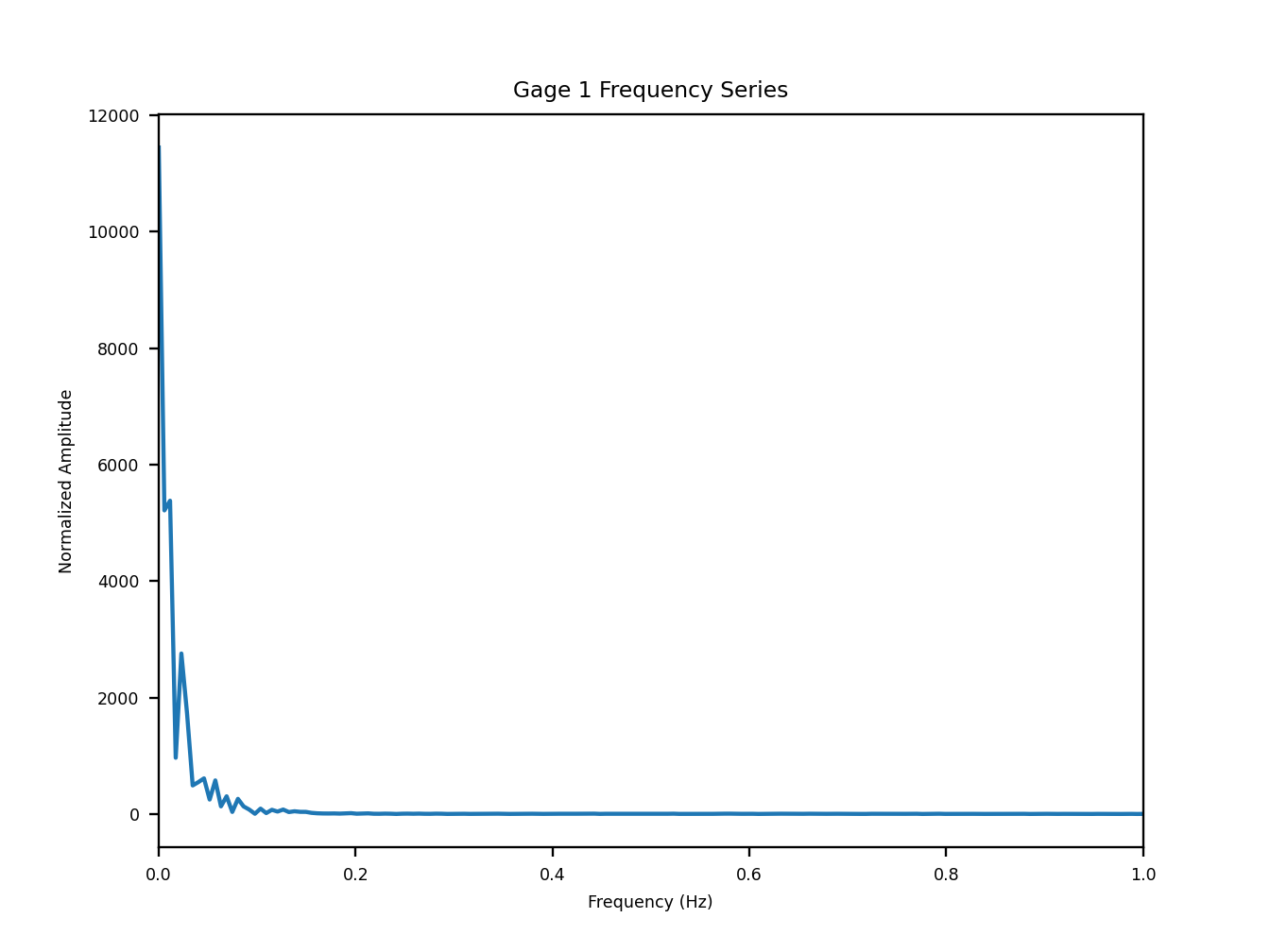
Fig. 18 An example of the diagnostic output provided by digger.analyze.spectrogram showing the frequency content.¶
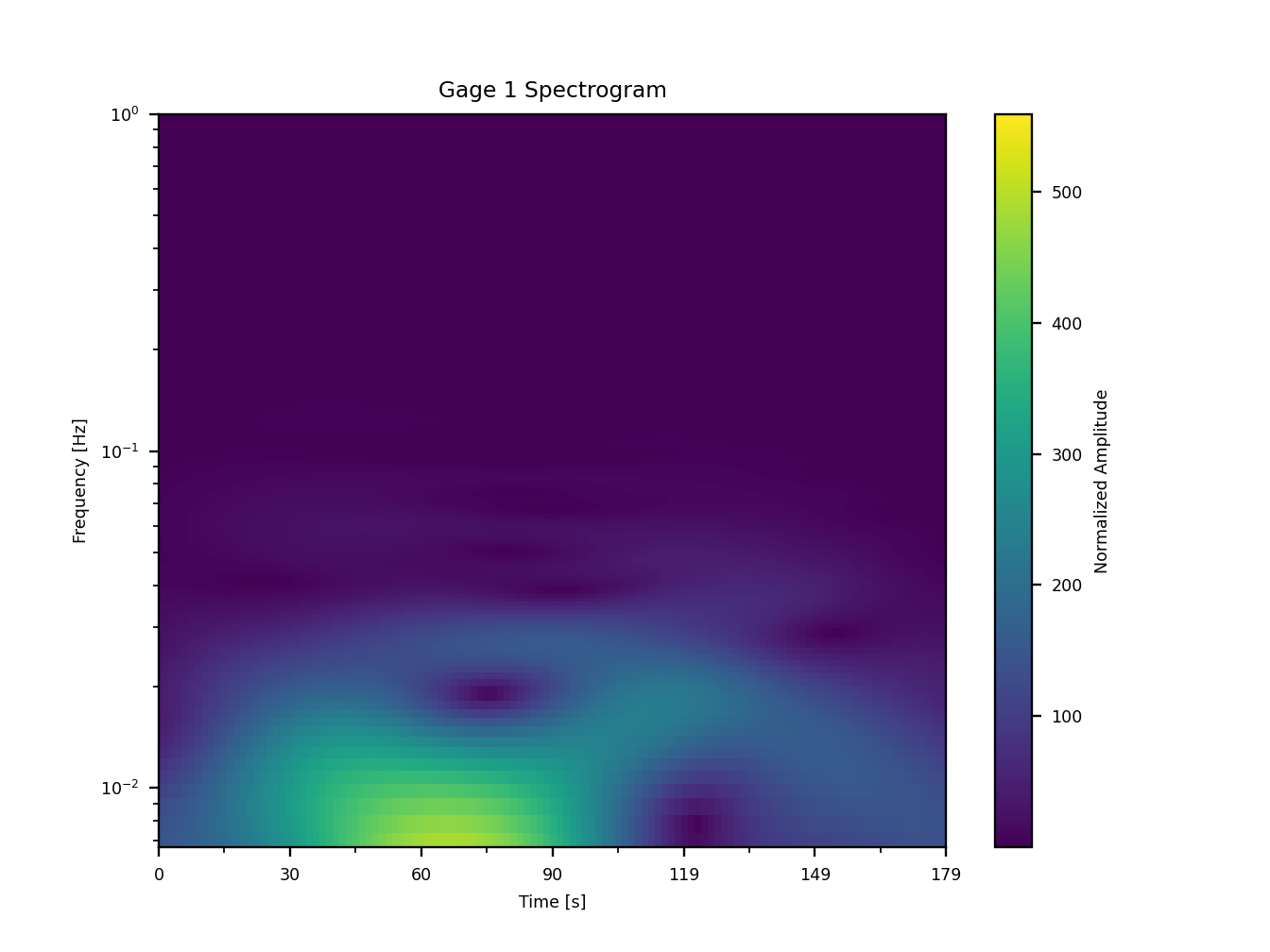
Fig. 19 An example of the diagnostic output provided by digger.analyze.spectrogram showing the spectrogram.¶